ABOUT PLURIPOTENT STEM CELL TECHNOLOGY
MAJOR ADVANCES INFLUENCING REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
REPROGRAMMING
We can now convert adult human cells, such as skin or blood, into stem cells that have properties of embryonic stem cells. The cells are known as human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and are capable of both self-renewing indefinitely and dividing into potentially any cell type in the human body.
GENE EDITING
Recent technology, referred to as gene editing, allows scientists to manipulate genomic DNA in human cells, including human iPSCs. This tool allows the capability to correct or insert disease-associated mutations for the development of personalized cell therapies and/or disease mechanism studies.
DIFFERENTIATION
Our ability to alter a human iPSCs into different cell types of the body is a process known as differentiation. Combined with reprogramming, differentiation enables the ability to derive disease-relevant cell types in unlimited quantities, including cell types that are normally difficult or risky to obtain from patients.
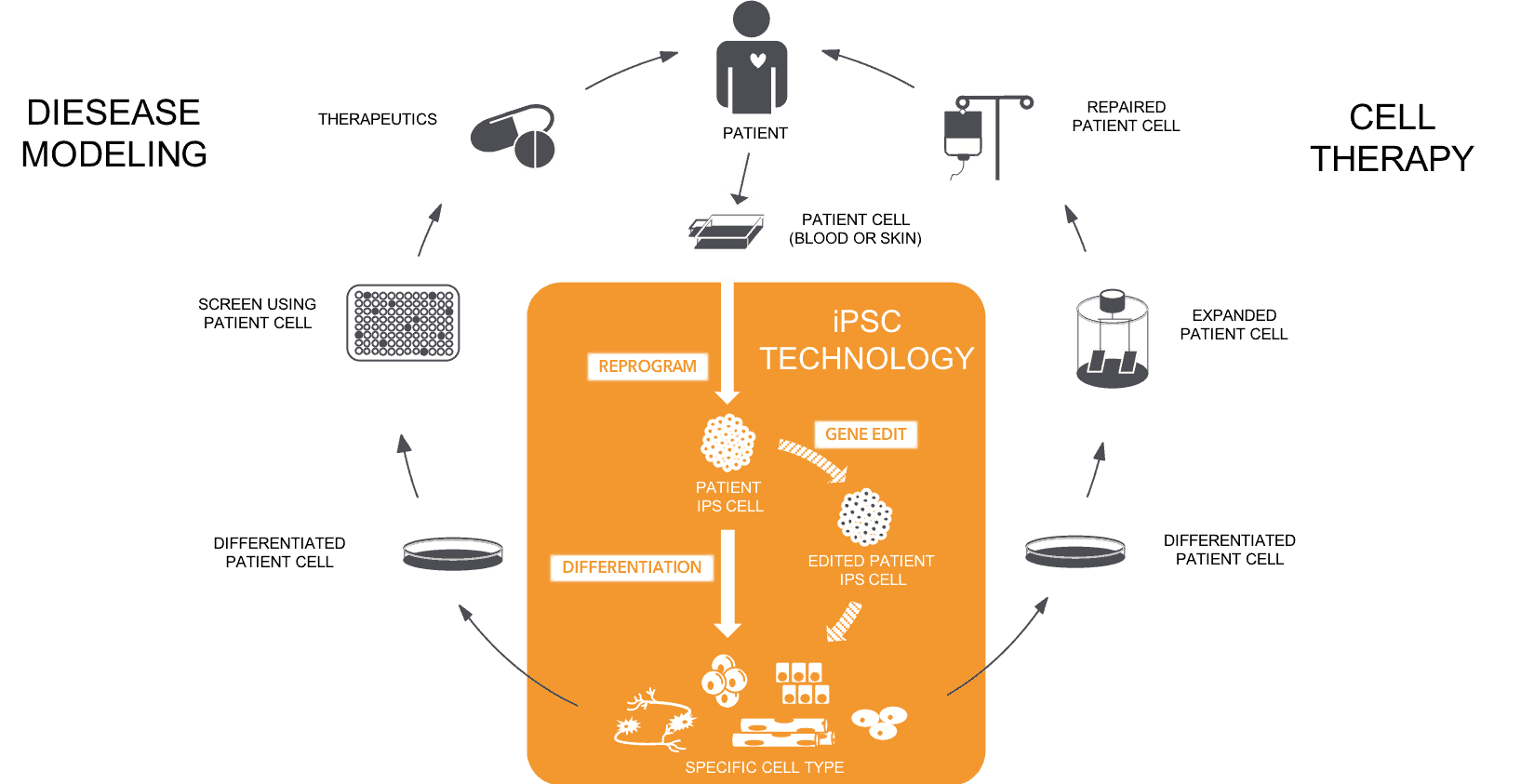
APPLICATIONS FOR DISEASE MODELING AND CELL THERAPY
Biopsies from affected or unaffected patients are first collected and cultured. Isolated cells are then reprogramming into iPSCs where they can be expanded and cryopreserved. iPSC lines can then be gene edited to alter the DNA to either remove or insert various diseases DNA coding regions. The gene modified hiPSC line can then be differentiated into the cell types of interest for disease modeling or transplanted back to the original patient via cell therapy.
PRINCIPAL ADVANTAGES OF HIPSCS FOR DRUG DISCOVERY
PATIENT SPECIFICITY
Human iPSCs can be
derived from patient cells
MOLECULAR
CHARACTERIZATION
Disease MOA
Functional Genetics
Patient Stratification
SCALABILITY
Human iPSCs can
self-renew indefinately
COMPLEX
IN VITRO BIOLOGY
3D Modeling
Interconnected Cell Systems
Spatial/Temporal Biology
DISEASE RELEVANCE
Human iPSCs can differentiate
into nearly all tissues of the body
PHARMACOLOGICAL
CHARACTERIZATION
Biomarkers
Drug Efficacy
Drug Toxicity
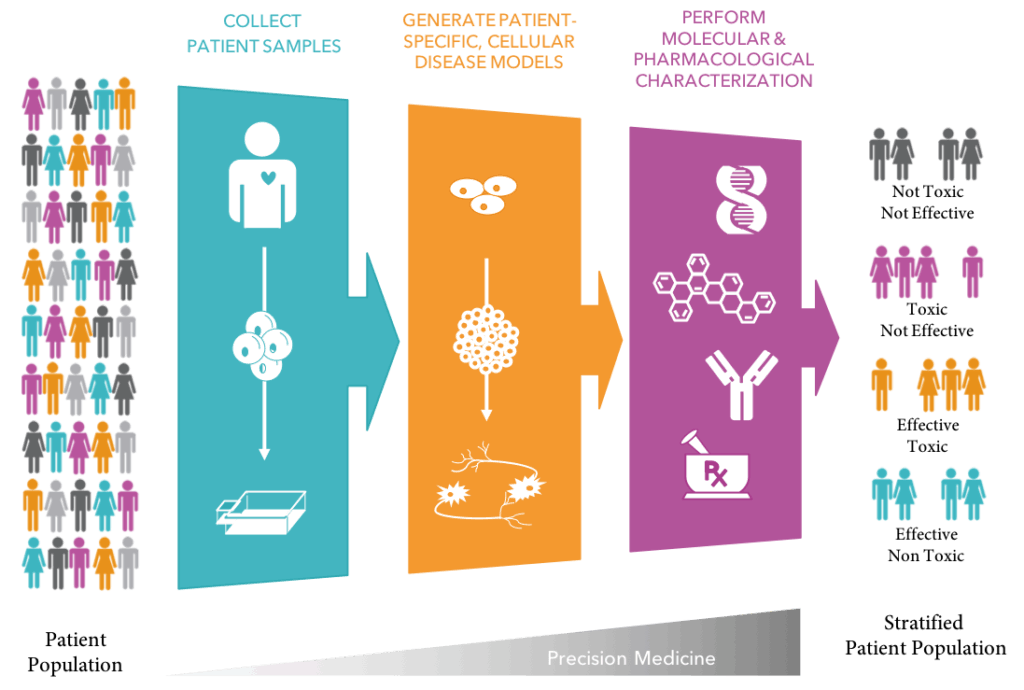
PATHWAY BIOLOGY IN THE CONTEXT OF PATIENT BIOLOGY
PATHWAY BIOLOGY AT THE SCALE OF A PATIENT POPULATION
PATIENT STRATIFICATION FOR MORE EFFECTIVE CLINICAL TRIALS
IMPROVED DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS & BIOMARKERS
PERSONALIZED MEDICINE WITH INCREASED EFFICACY & LOWER TOXICITY